
Aloe vera plants have been used for centuries for health and beauty. In ancient Egypt, this plant was called the ‘plant of immortality’. It is often described as a wonder plant due to its several health benefits.
Read on to know about the impressive health benefits of aloe vera and its side effects!
Aloe vera is a short-stemmed shrub, and the gel obtained from the plant’s leaf is the main ingredient used in beverages, skin lotions, and cosmetics. It mainly grows in the dry regions of Africa, Asia, Europe, and America. In India, aloe vera is mainly found in Rajasthan, Andhra Pradesh, Gujarat, Maharashtra, and Tamil Nadu.
It is called ‘Ghritkumari’ in Hindi, ‘kalabanda’ in Telegu, ‘lolisara’ in Kannada, and ‘ghrtakumar’ in Bengali. The word aloe vera comes from the Arabic word "Alloeh,” meaning “shining bitter" substance, whereas “vera” is a Latin word meaning “true.”
– Wild species of aloe vera can survive up to 100 years.
– There are around 250 species of aloe vera but only 4 of them are cultivated for their health benefits.
– The Egyptian queen Cleopatra was said to apply aloe vera gel as a part of her beauty ritual.
_1729581993.webp)
Various traditional branches of medicine, like Ayurveda, Chinese medicine, and modern British herbal medicine, have advocated aloe vera for its healing properties. Even so, many claim that Alexander the Great conquered the island of Socotra, off the coast of Africa, to secure supplies of aloe vera to treat wounded troops.
The 10 Health Benefits of Aloe Vera
The translucent gel contains up to 99% water, and the rest consists of glucomannans, amino acids, lipids, sterols, and vitamins. Aloe vera contains vitamin A, vitamin B12, vitamin C, and vitamin E. It also contains calcium, magnesium, zinc, chromium, selenium, iron, potassium, copper, and manganese. It provides at least seven of the nine essential amino acids and many non-essential amino acids too, which are important for human health.
Let’s look at some of the major health benefits of aloe vera.
Reduces Cholesterol
A few studies suggest that aloe vera can play a role in lowering cholesterol. According to the National Institute of Health (NIH), a daily intake of 10 to 20 ml of aloe for 3 months can reduce LDL (bad) cholesterol by 18% and total cholesterol by 15%.

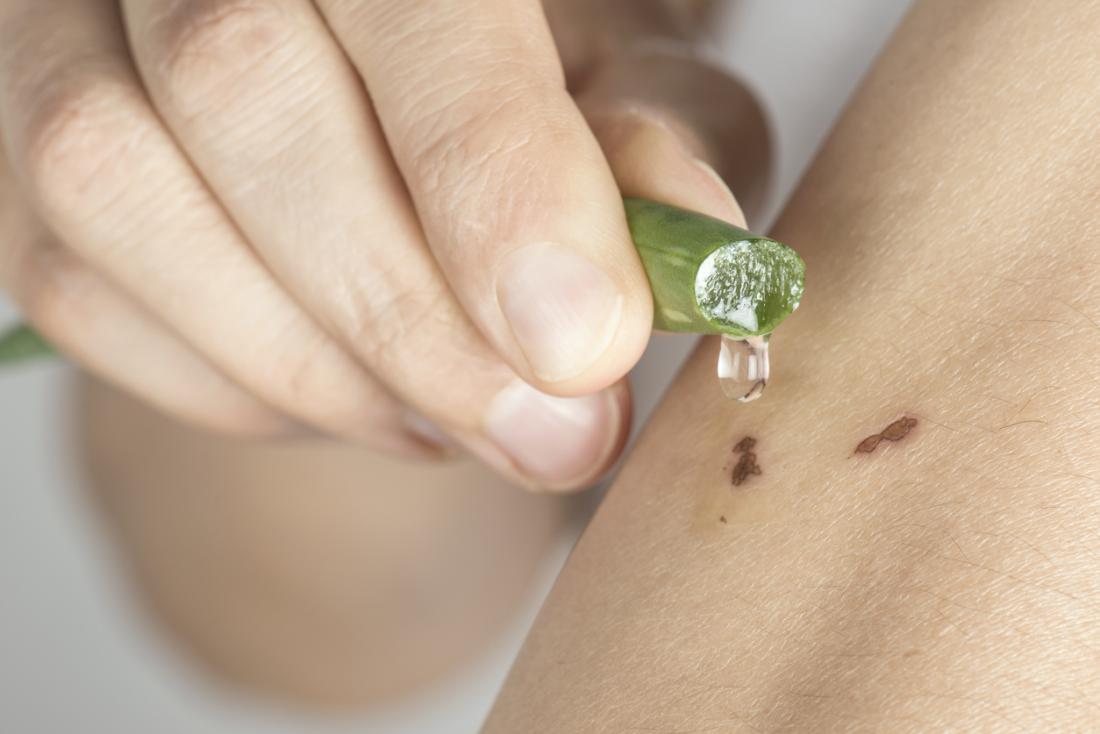
Aids Wound Healing
Aloe vera contains the hormones auxins and gibberellins that help in wound healing and have anti-inflammatory properties. Glucomannans (a polysaccharide) and gibberellins increase collagen synthesis by stimulating fibroblast activity and proliferation. The fibroblast is a type of cell that produces collagen and other fibers essential for tissue repair.
Maintains Heart Health
Aloe vera leaf gel reduces serum cholesterol and triglyceride levels and increases HDL levels. Researchers have found that aloe vera gel easily stimulates the fibroblasts to make new tissues. The stimulation of fibroblasts leads to the formation of proteoglycans and collagens, which reduces the risk of cardiovascular disorders.
Improves Digestion
Aloe vera is a prebiotic super-food because it feeds the beneficial bacteria in the gut which helps in maintaining a healthy microbiome. It also helps in controlling stomach ulcers. Additionally, Aloe vera juice may help treat irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and other inflammatory disorders of the intestine.

Strengthens Immunity
One of the unexpected health benefits of aloe vera is improving your immunity. Aloe vera effectively works as a cellular regenerator and offers antibacterial and antifungal benefits. It is also a strong antioxidant, as the juice activates the cells to produce nitric oxide and cytokines. As a result, this helps the immune system fight free radicals that can cause cancer and other diseases.

Reduces Inflammation
The high content of fatty acids in the herb has the ability to decrease healing time for second- and third-degree burns. Due to its antimicrobial properties, it also helps to reduce bacterial colonization, preventing skin infection.

Aids Detox
The good thing about including gelatinous plant foods such as aloe vera in your diet is that the gels from these plants move through the intestinal tract easily. They absorb toxins along the way and eliminate them through the colon. As a result, this helps in the proper elimination of waste from your body, thus detoxifying it.

Studies conducted at the University of Las Palmas de Gran Canaria, Spain, in May 2013 determined that the methanol extract of the leaves and flowers of aloe vera may have beneficial effects on human health. The reports show that both aloe vera flower and leaf extracts have antioxidant properties, especially the leaf skin extract. The leaf skin extract also has anti-mycoplasmic properties (the ability to destroy bacteria).
Enhances Skin Health
Aloe vera soap and gel contain several nutrients, such as glycerin, sodium palmate, sodium carbonate, sodium palmate, and sorbitol, which nourish the skin. They are also rich in various vitamins and beta-carotene, which slows down visible signs of aging, such as wrinkles, dark spots, and dullness.
Treats Hemorrhoids
Aloe vera is an effective treatment for piles. The anti-inflammatory properties of aloe vera reduce inflammation as well as alleviate bowel irregularities and intestinal problems. It also makes the stool soft and easy to pass. Additionally, anthraquinones, one of the key compounds present in aloe vera, help stimulate contractions on the walls of the digestive tract.

Improves Hair Health
Aloe vera contains enzymes called proteolytic enzymes, which repair the dead skin cells on the scalp. It also reduces dandruff and hair fall and acts as a great hair conditioner. The primary protein of hair is keratin, which consists of amino acids, oxygen, and carbon, as well as small amounts of hydrogen, nitrogen, and sulfur. The chemical makeup of aloe vera is similar to that of keratin, which rejuvenates the hair with its nutrients, making it more elastic and preventing breakage.
Click here to know about foods that improve hair health!
Ways to Use Aloe Vera
Aloe produces gel and latex, which are used in medicine production. Aloe gel (a clear, jelly-like substance) is present in the inner parts of the aloe leaf, whereas aloe latex is yellow in color and is present just under the plant’s skin. You can eat it orally as a laxative to get relief from constipation.
Here are a few other ways in which you can use aloe vera in your daily life:
- Aloe vera benefits your skin immensely. For dry skin, take some aloe vera and add a pinch of turmeric and a teaspoon of honey and milk, along with a few drops of rose water. Apply it and leave for 20 minutes.
- You can also use it for the treatment of acne due to its antioxidant properties. Mix aloe vera gel, blended walnuts, and honey and apply it to the skin for smooth and clear skin.
- You can drink aloe vera juice to make your body healthy and fit, as it will make your body alkaline. A body with an acidic pH is a breeding ground for various diseases and ailments.
- To keep your liver healthy, it is good to drink aloe vera juice, as it is rich in phytonutrients and keeps the body hydrated.
- Apply aloe vera gel for quick healing of burns.

Are there any Side Effects of Aloe Vera?
Some possible side effects of aloe vera are:
- Latex in the aloe vera leaves may trigger an allergic reaction in those who are sensitive to latex, causing stomach issues like irritation, stomach cramps, and low potassium. The gel of aloe vera may also cause skin allergies and redness on the skin.
- Since aloe vera contains latex, consuming aloe vera juice may cause your blood sugar levels to drop and may lead to an electrolyte imbalance in diabetics.
- The laxative effects of aloe vera can lead to dehydration. Laxatives generally alleviate constipation; however, consuming more than the recommended dosage may cause dehydration.
- Pregnant women should avoid drinking aloe vera juice as it can stimulate uterine contractions and could even lead to miscarriage.
- Due to its laxative effects, lactating mothers should avoid drinking aloe vera juice, as it can give their babies vomiting and diarrhea. In fact, all children under the age of 12 should avoid consumption.
- Aloe vera juice may lower the levels of potassium in the body, causing an irregular heartbeat, weakness, and fatigue. Thus, the elderly and sick people should avoid it.
- The latex can cause excessive cramps and stomach pain, which is one of the most common side effects of drinking aloe vera juice. It is advisable not to consume aloe vera juice if you are dealing with stomach issues.
- Using aloe vera gel on the skin for a long period of time can lead to allergic reactions, including hives or an eczema-like rash.
- Aloin is a natural chemical present in the skin of Aloe vera that has laxative effects. However, its side effects are overstimulation of the bowels, dehydration, severe diarrhea, abdominal cramps, dramatic weight loss, and electrolyte imbalance.
Thus, it is completely safe to consume the pure inner gel of aloe vera without any side effects, which is the main nutrient powerhouse.
Recommended Dosage
There is a lack of research to determine the recommended dosage. In the only human study conducted, aloe extract of 300 mg twice a day was administered with reported benefits and no side effects. Individuals who want to use aloe vera should follow the recommended dosage on package labels. Suggested daily doses are:
-60 ml of aloe vera juice twice a day (120 ml total).
-300 mg of aloe supplement twice a day (600 mg total).
-Raw aloe vera gel – 60 ml.
-15 ml of aloe juice or gel twice a day (30 ml total) for diabetics.
-100 ml aloe gel, twice a day for 4 weeks for IBS.


.png)


