
We are all familiar with the term pollution and always hear about its harmful effects on both the environment and our health. With growing urbanization and industrialization, air pollution has become a silent killer. India has the highest death rate due to air pollution, with cities like Delhi being compared to a “gas chamber." It is probably one of the most serious environmental problems affecting our entire civilization today. Thus, the prevention of air pollution is the need of the hour. But before that, it’s important to understand how it affects our health.
Read on to learn how to protect yourself from air pollution!
Life exists on Earth due to a combination of gases that collectively form the atmosphere. An imbalance caused by an increase or decrease in the percentage of these gases can be harmful to survival. Air pollution occurs when any harmful gases, dust, or smoke enter the atmosphere and make it difficult for plants, animals, and humans to breathe and survive.

Air Pollution Causes
Various factors are responsible for releasing pollutants into the atmosphere. These sources can be classified into two major categories: man-made sources and natural sources.
Man-made Sources
Major sources include the burning of fossil fuels, agricultural activities, exhaust from factories and industries, mining operations, and the use of automobiles. In some regions, waste burning and deforestation are additional sources of air pollution.

Natural Sources
It includes dust, smoke, wildfires, volcanic eruptions, carbon dioxide released respiration, and methane released from cattle digestion.
/GettyImages-608873707-f359835d93ea4f0b95a50cbeeb839c05.jpg)
Types of Air Pollutants to Look Out For
Every material in the air that could affect human health or have a profound impact on the environment is defined as an air pollutant. According to the World Health Organization (WHO), there are six major air pollutants that harm human health and the environment. They are:
- Particulate Matter (PM)
- Ground-level Ozone
- Carbon Monoxide (CO)
- Sulfur Oxides
- Nitrogen Oxides
- Lead (Pb)

Other pollutants from suspended materials such as dust, fumes, smoke, mists, gaseous pollutants, hydrocarbons, and Volatile Organic Compounds (VOCs) present in the air at high concentrations can increase the risk of many diseases, such as respiratory disorders, heart diseases, Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD), stroke, and different types of cancer.
Who is most at Risk?
Air pollution is a concern for all of us. However, certain groups of people are sensitive to common air pollutants like particulates and ground-level ozone. Reactions to air pollutants depend on the type of pollutant a person is exposed to, the individual’s health status, genetics, and the degree of exposure.
People at an increased risk of air pollution include:
- Individuals with heart disease, coronary artery disease, or congestive heart failure
- Pregnant women
- Outdoor workers
- Older adults and the elderly
- Children under age 14
- Athletes who exercise vigorously outdoors
- Individuals suffering from lung diseases such as asthma, emphysema, or COPD.
How does Air Pollution Affect your Health?
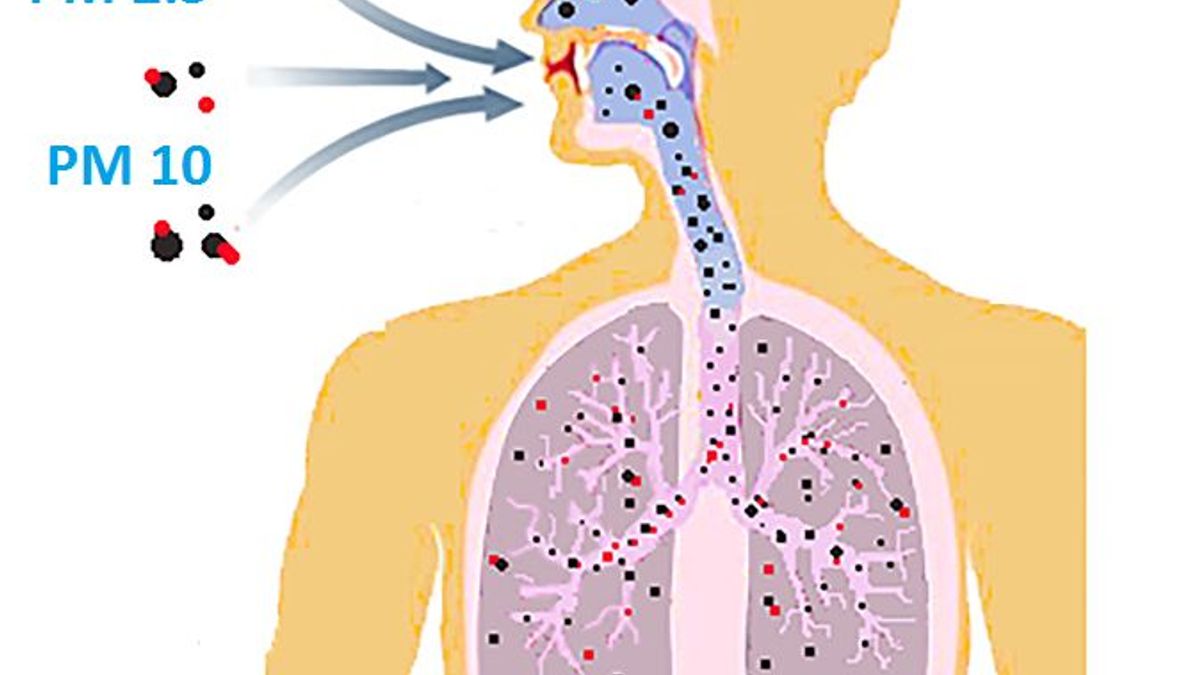
The finer the particle, the longer it is suspended in the air and the easier it is to become airborne in the wind. It can be fine, solid, or liquid particles. When these particles enter our bodies, they can have both short-term and long-term adverse effects on our health.
PM 10 vs PM 2.5
Particulate matter is the most studied air pollutant that can affect your health and cause respiratory and cardiovascular diseases. The WHO defines air quality based on two measures: PM10 and PM2.5. PM10 is particulate matter in the air that is 10 micrometers in diameter or less. On the other hand, PM2.5 is 2.5 micrometers in diameter or less, often described as fine particles or aerosols.
Short-Term Effects
The immediate effects of air pollution include:
- Irritation of the eyes, nose, and throat
- Wheezing and coughing
- Chest tightness
- Breathing difficulties
Long-Term Effects
Some symptoms of long-term exposure to polluted air are:
- Accelerated aging of the lungs
- Decreased lung function
- Loss of lung capacity
- Worsening of existing lung and heart problems or development of diseases such as asthma, bronchitis and emphysema
- Shortened life span
- Increased risk of heart attack and cancer

According to the WHO, an estimated 7 million people die every year from exposure to fine particles in polluted air that penetrate deep into the lungs and cardiovascular system. It can cause diseases like stroke, heart disease, lung cancer, chronic obstructive pulmonary diseases, and respiratory infections, including pneumonia.
Pollutants such as nitrogen dioxide and particulate matter from road traffic, as well as sulfur dioxide from the burning of fossil fuels, have been linked to suppressed lung growth in children, asthma, heart disease, and the onset of type 2 diabetes.
In pregnant women, air pollution can trigger inflammation throughout the body, including the uterus, which can increase the risk of preterm birth. It has also been found to affect fetal brain development. Additionally, air pollution can have serious effects on neural functioning and neural matter by permanently affecting vascular structures in your brain. Studies show that living in areas of high pollution has serious long-term health effects, especially for children and adolescents, as it can diminish mental capacity and increase the risk of brain damage.
Long-term exposure to air pollution affects people of all ages and can cause cancer. It can also cause damage to the immune, neurological, reproductive, and respiratory systems. In extreme cases, it can even cause death. Thus, the prevention of air pollution is of utmost importance.
Protect Yourself from Air Pollution
The most effective way for the prevention of air pollution is to avoid producing it in the first place. Therefore, start by checking and monitoring your emissions.
To protect yourself from air pollution you can follow these below-mentioned tips:
- Avoid morning walks, jogging, or exercising in the heavily traffic-loaded areas.
- Go off the streets in the scorching heat. High temperatures reduce the quality of the air.
- Avoid and discourage smoking indoors.
- You can also use air-purifying plants to reduce indoor air pollution.
- If you are living in an area with high air pollution, install air filters in your house.
- Wear air pollution protection masks whenever you go out.
- Keep the air filters of your air conditioners and ventilators clean and dust-free.
- Include antioxidant- and anti-inflammatory-rich foods in your diet. These foods help you fight inflammation and oxidative stress caused by long-term exposure to air pollution.
- Avoid burning fireworks and wood fires.
- Carpool or use public transportation as much as possible.

Conclusion
The World Health Organization stated in 2014 that air pollution causes the premature death of an estimated 7 million people worldwide every year. Therefore, the prevention of air pollution is vital and should be a top priority for governments across the world. To protect themselves from air pollution, everyone should be more aware of the implications of their daily activities on both the environment and their health. Without a healthy environment, leading a healthy life is impossible.


.png)


