.jpg)
Aging is an irreversible part of our lives. We all age. However, some people can age faster. This can occur due to several factors such as an unhealthy lifestyle, diet, stress, and even genetics. To slow down the process of aging, it is imperative to know how the process of aging works. Here we tell you all about Anti-Aging, Redox Signaling, and Glutathione.
Read on!
What Causes Aging?
Aging is an irreversible process that affects all of us. However, there are certain factors that can speed up the process of aging. Aging is a multi-factorial process that occurs due to genetic and environmental factors. Factors such as an unhealthy diet and stress also affect aging. Aging affects physiological functions and occurs due to the accumulation of damage in molecules, cells, and tissues over a lifetime. It is partly occurring due to oxidative stress.
Oxidative stress occurs when there is an imbalance between antioxidants and free radicals in the body. Antioxidants are phytochemicals (biologically active compounds in plants), vitamins, and minerals that inhibit oxidation or free radical production. Free radicals are positively charged and chemically unstable particles that are in dire need of binding to anything they lay their hands on by stealing an electron.

At a cellular level, aging occurs due to cell senescence, a consequence of exposure to intrinsic and extrinsic aging factors. It is characterized by the gradual accumulation of DNA damage and epigenetic changes in DNA structure. This results in an exponential increase in the incidence and mortality rates of cancer and other life-threatening diseases. The accumulation of DNA damage over time leads to mutations in the body.
Mutations are the alteration of single base units in DNA or the deletion, insertion, or rearrangement of larger sections of genes or chromosomes. Additionally, age-related disorders can lead to telomere shortening. Telomeres are DNA-protein complexes that cap the ends of linear DNA strands, stabilizing them and preventing chromosome instability. They become critically short after repeated mitotic divisions without adequate telomerase activity, making cells susceptible to apoptosis, death, and mutations. Telomere shortening, in turn, impairs stem cell function and causes premature aging, thus starting a never-ending cycle.

Know about the role of antioxidants in anti-aging here!
Role of Redox Signaling in Anti-aging
All the events in a cell occur due to a complex array of chemical reactions that occur inside the cell in a variety of patterns. This is referred to as cellular signaling. Cellular signaling plays a pivotal role in almost every aspect of life, including growth, health, disease, aging, and even cancer. Redox signaling regulates the most critical cellular signaling pathways in our body. It involves specific reactions that regulate a myriad of biological processes, such as neurotransmission, homeostasis, and apoptosis. Any disbalance in the redox reactions occurring inside the cell can disrupt many of its biological processes.
As a person ages, the redox processes occurring inside the cells weaken, and thus, with time, the robustness of the cells declines. This is why the risk of cancer and other life-threatening diseases increases with age. One of the main reasons the redox processes in the cell weaken is because the proportion of the redox molecules is affected. Some are produced less, while others are produced more. Antioxidant molecules such as glutathione, which play a critical role in regulating and moderating these redox processes inside a cell, are also affected.
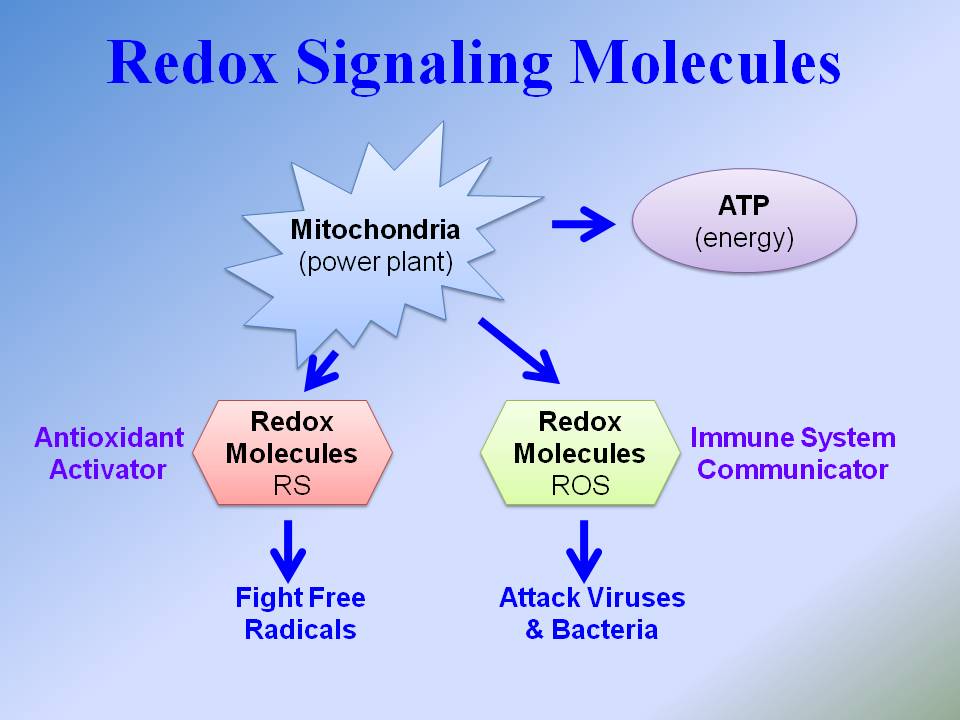
Thus, redox signaling formulations can have anti-aging benefits. Other benefits include:
- Supplements redox signaling carriers which help in intra and intracellular communications.
- Allows quicker detection during cell damage.
- Signal for quicker replacement of damaged cells.
- Signal for quicker and more precise immune response.
- Clarifies signals needed for regenerative processes.
- Normalizes the proper redox potential needed to optimize signaling in all cellular fluids and receptors.
- Increases the levels of Glutathione.
Role of Glutathione and Its Benefits
Glutathione is one of the main non-protein antioxidants in the cell. It plays a critical role in anti-aging. Glutathione plays a key role in the protection against free radicals that result from aging. According to a study published in Clinical, Cosmetic, and Investigational Dermatology (2017), glutathione has various beneficial effects on skin properties and is possibly an anti-aging agent. It also plays a detoxifying role in the body by neutralizing the free radicals generated during the first phase of liver metabolism.

Other benefits of glutathione include:
- Increasing energy levels.
- Reducing muscle and joint discomfort.
- Strengthening the immune system.
- Improving mental focus and clarity.
- Improving the quality of sleep.
- Reducing the effects of stress.
- Improving skin health.
- Enhancing athletic performance and recovery.
Oxidative damage to DNA is directly related to the oxidation of glutathione. In fact, aging results from oxidative damage to proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. These molecular lesions may be the reason behind the low physiological performance associated with aging. Thus, glutathione supplementation may be a rational way to partially protect against age-related impairment in performance.
Clearly, there is a wide range of benefits to glutathione. Studies suggest that taking glutathione in supplemental form can have a positive effect on overall health. According to a 2015 study published in the European Journal of Nutrition, daily supplementation with glutathione can lead to higher stores of glutathione in the body. They also reported multiple improvements in immune function, including a twofold increase in natural killer cell cytotoxicity in patients who took a higher dose of glutathione. Therefore, this indicates that supplementation can have clinically significant effects that directly impact your health.


.png)


