
The human body needs calcium during all its life stages. From a fetus to old age, our body essentially needs calcium for growth and maintenance of healthy bones. However, with so many fancy diets around us, we often tend to miss out on calcium-rich foods. Apart from providing healthy bones for life, calcium offers several other health benefits.
Read on to know more!
Why is Calcium Important for Us?
Calcium forms 2% of the total body weight of an adult. It is found in our bones and teeth in high volumes. Traces of calcium are also present in our blood, which prevents life-threatening hemorrhages. Calcium has several critical biological roles in the body, which include maintaining healthy bones and joints, dental health, preventing colon cancer, and reducing obesity, among others.

Key Benefits of Calcium
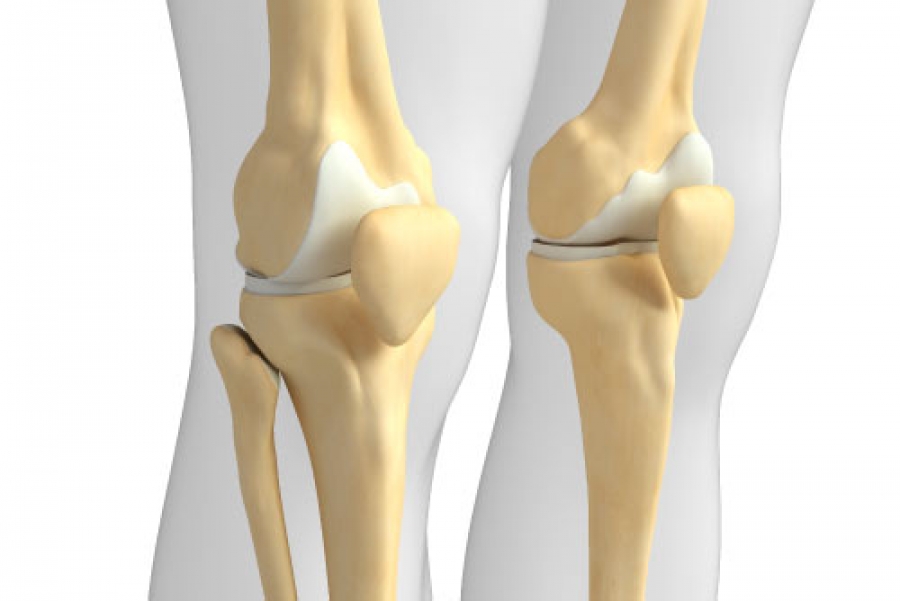
Healthy Bones
Calcium, together with other essential minerals like Vitamin K and Vitamin D, is required to maintain bone mineral density and prevent weak, brittle bones and fractures. It helps form a part of hydroxyapatite, the mineral complex that makes your bones and teeth hard and maintains bone health. Without enough calcium, the bones become weak and fragile and are therefore more prone to fractures and breaks.
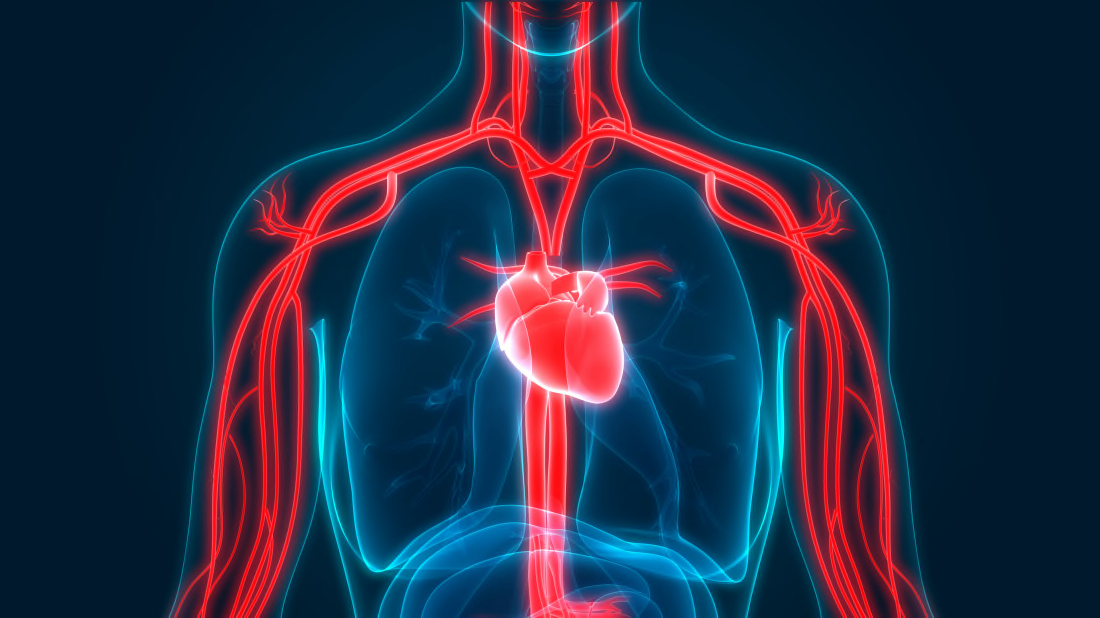
Cardiac Health
The cardiac muscles (which make up our heart) require calcium ions to contract and relax properly at a biochemical level. Thus, calcium makes the normal functioning of the cardiac muscles possible.
It also helps the nervous system maintain proper pressure in the arteries. If there is a drop in the body's calcium concentration, a hormone called calcitriol is released, which contracts the smooth muscles of the arteries, thereby increasing blood pressure.
Colon Cancer Prevention
Adequate calcium intake can prevent the risk of colon cancer and suppress the growth of polyps (a small, usually benign, growth from the mucous membrane) that can lead to cancer. Calcium supplementation also reduces the risk of adenomas (a benign tumor formed from glandular structures) and nonmalignant tumors of the colon. The excess calcium left in the intestines after the body absorbs what it needs is believed to bind to the cancer promoters, so they’re excreted together from the body.

Dental Health
Calcium not only provides healthy bones for life but also maintains dental health. Calcium protects the teeth by keeping the jaw bone strong and sturdy throughout life, which ensures tight-fitting teeth where bacteria cannot thrive. Thus, before teeth and gums start giving any trouble, be sure to maintain a calcium-rich diet. Calcium intake should be high, especially at a young age, so that children can grow up with strong teeth.
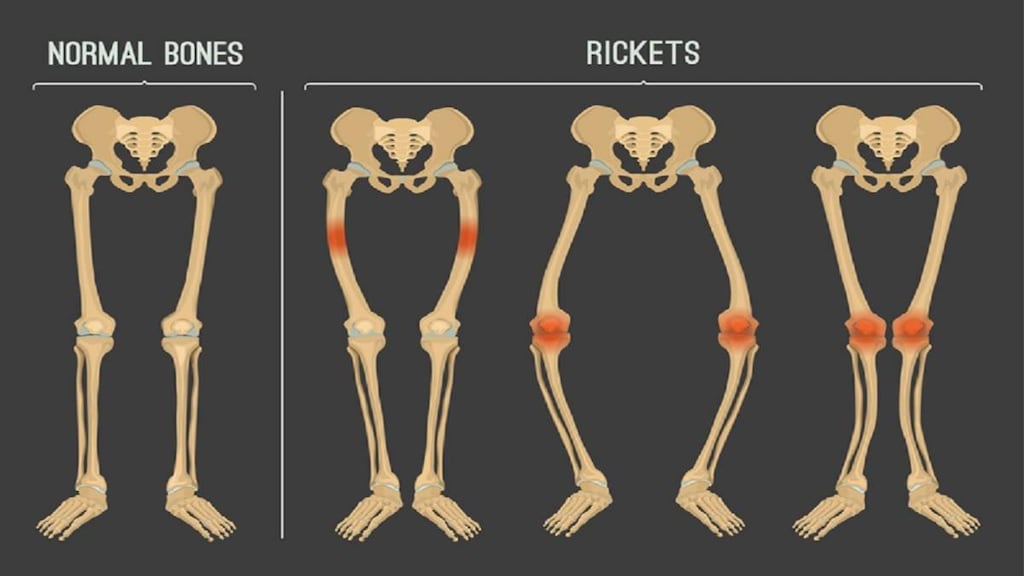
Calcium Deficiency Symptoms
Some symptoms of calcium deficiency are:
- Heart palpitations or abnormal heart rhythms
- Tooth decay or periodontal disease
- Brittle or misshapen nails
- Higher cholesterol levels
- Insomnia
- Lethargy or chronic fatigue
- Poor appetite
- Confusion
In some severe deficiency cases, calcium deficiency can result in diseases such as:
- Osteoporosis: A condition when bone density decreases and the body stops producing as much bone as it did before.
- Rickets: A childhood bone disorder where bones soften and become prone to fractures and deformity.
- Osteonecrosis: The death of bone tissue due to a lack of blood supply.
- Tetany: A condition in which nerve activity becomes excessive and causes spasmodic contractions of skeletal muscles.
Can Excess Calcium be Unhealthy as well?
Consuming too many calcium supplements and certain diseases can lead to high calcium levels in the blood. But most of the time, it is the result of thyroid dysfunction, a condition known as hyperparathyroidism.
Normally, our parathyroid gland produces hormones that regulate optimal calcium levels in the body. High levels of this hormone can lead to calcium being released from the bones into the blood. As a result, this can weaken the bone structure, causing bone deformities and other severe problems.
Some symptoms of a calcium overdose are loss of appetite, nausea, vomiting, kidney stones, frequent urination, and an irregular heartbeat. Excessive calcium in the body also hinders the absorption of essential minerals like iron and zinc.
How to Include Calcium in your Diet?
Calcium can help you provide healthy bones for life. The biggest sources of calcium include milk and dairy products such as yogurt, cottage cheese, and curd. Other foods for strong bones and muscles include fish with bones, soy, and soy products. Apart from milk products, other good dietary sources of calcium include almonds, orange juice, dried figs, green leafy vegetables, fortified cereals, and some dried beans.

Some common calcium-rich Indian dishes are Paneer Parantha, Rajma (kidney beans), Palak Paneer, Lassi, Kheer, Chole (chickpeas), and many more. You can also make different milkshakes and smoothies using full-fat or low-fat milk to get sufficient calcium in your diet. Additionally, you can snack on your favorite nuts in between meals to increase your calcium intake.
Also, remember to include sufficient vitamin D-rich foods in your diet, as it helps your body effectively absorb calcium from foods. Some vitamin D-rich foods are fatty fish, beef liver, egg yolk, cheese, mushrooms, and foods fortified with vitamin D.
Daily Recommendation
The Recommended Daily Allowance (RDA) for Calcium is 600 mg for healthy adults and 1200 mg for pregnant and lactating women as per the National Institute of Nutrition, Hyderabad.


.png)


