
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is the fifth-leading cause of death worldwide, causing 3.17 million deaths globally in 2015 alone (source: WHO). It is an inflammatory lung disease that causes obstructed airflow from the lungs and makes it hard to breathe. Symptoms include breathing difficulty, coughing, mucus (sputum) production, and wheezing. People with COPD are at a higher risk of developing heart disease, lung cancer, and a variety of other health issues. Thus, to increase the quality of life and reduce COPD-related complications, nutritional support is highly recommended.
What causes Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease?
COPD is caused by long-term exposure to irritating gases, smoking, and particulate matter. The main causes of COPD include smoking (both active and passive), smokers with asthma, occupational exposure to chemicals, fumes, and particulates, exposure to smoke while cooking (especially in rural areas), age, genetic makeup, and high pollutant concentrations in big cities.
COPD is marked by a high concentration of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in the lungs and less availability of antioxidants. ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS) are major causes of oxidative stress. Reduction of antioxidants in the body and increase of free radicals (ROS, RNS) leads to oxidative stress. This, in turn, interferes with cellular signalling, leading to progressive inflammation and a reduction in the body’s natural defenses. This imbalance may then provoke pathological reactions, causing a range of respiratory diseases, particularly chronic obstructive pulmonary disease.
Symptoms
As the name suggests, COPD is a chronic disease and often doesn’t appear until significant damage has occurred.
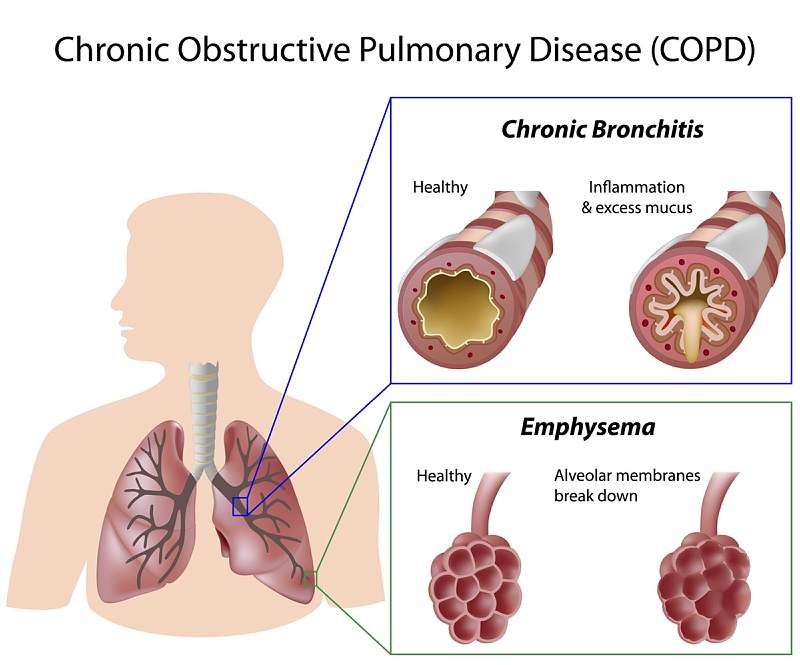
COPD is a progressive lung disease. It is difficult to identify the disease in its early stages due to common symptoms such as cough and cold. The most common manifestations of COPD are emphysema (a lung condition that causes shortness of breath) and chronic bronchitis. Many people with COPD have both of these conditions.
- Chronic bronchitis is an inflammation of the lining of the bronchial tubes, which carry air to and from the air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs. It is characterized by a daily cough and mucus production.
- Emphysema is a condition in which the alveoli at the end of the smallest air passages (bronchioles) of the lungs are destroyed as a result of damaging exposure to cigarette smoke and other irritating gases and particulate matter.
In the case of smokers and individuals with regular exposure to particulates, the condition becomes severe with time. The main symptom is a daily cough with mucus. Other symptoms include chest tightness, shortness of breath even during minor physical activities, an early morning choked throat, frequent respiratory infections, weight loss with the progression of the disease, etc.
Know more about the antioxidant food you should start eating today!
How can you manage COPD?
Currently, there is no cure for COPD. Conventional treatment with correct nutritional support helps ease the symptoms, improve the quality of life, and reduce the steady progression of related complications associated with COPD.
Current recommended treatment includes medications, oxygen therapy, and surgery. There are many nutraceuticals (a food or substance in food having medicinal or health benefits) that are rich in antioxidants and help in reducing the effects related to COPD. The source materials of these antioxidants are turmeric, citrus fruits, grapes, pine tree bark, fish and algae, fruits and vegetables with a high concentration of B-complex vitamins, vitamin C, vitamin E, trace metals, etc.
Following are a few of the nutraceutical ingredients that have shown clear indications for reducing the progression of respiratory disorders and countering the progressive complications related to COPD.
Pycnogenol
Pycnogenol is extracted from the pine bark and has multiple health benefits, including cardiovascular health, immunity support, cognitive health support, and controlling COPD progression.
In COPD, pycnogenols reduce the number of inflammatory cells and hence reduce overall inflammation. In a recent mouse study at the College of Veterinary Medicine (BK21 Plus Project Team), Chonnam National University, pycnogenol has shown clear benefits in containing the progression of COPD.
Polyphenols
Dietary polyphenols exert a wide range of beneficial biological functions beyond their antioxidant properties. It helps in the regulation of cell survival pathways, leading to anti-carcinogenic and anti-mutagenic functions. Green tea is a rich source of polyphenols, which are strong antioxidants.

Studies have found that polyphenols inactivate cellular oxygen radicals, and prevent membrane lipid peroxidation and DNA oxidative damage. Recent studies have also indicated that polyphenols have beneficial properties due to their interaction with cellular signalling pathways and related machinery that mediate cell function under both normal and pathological conditions.
Curcumin
Curcumin is a component present in turmeric, a spice widely used in Asia as an ingredient for curries. It has been used for centuries in Ayurveda (Indian traditional medicine) for the treatment of several diseases. Known for its numerous health benefits, it is widely used in creams, lotions, and other oral medicaments.
Curcumin in turmeric is used to treat many skin and digestive issues. It is known to have anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. For individuals suffering from COPD, curcumin mediates its anti‐inflammatory effects through the down‐regulation of inflammatory transcription factors and pro-inflammatory enzymes in the lungs.
Resveratrol
Resveratrol is a component largely present in red wine extract that has anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. It is known to have positive effects as an anti-aging drug with protective effects against lung cancer. It may also be used as an alternative to corticosteroids (cortisone-like medicines) in COPD therapy.

Resveratrol inhibits the release of one of the major chemicals (interleukin-8) known to cause inflammation in smokers and patients with COPD. Some other sources of resveratrol are peanuts, pistachios, grapes, white wine, blueberries, cranberries, and even cocoa and dark chocolate.
Omega-3 Fatty Acids
Docosahexaenoic acid (DHA) is an omega-3 fatty acid present in fatty fish, flax seeds, seaweed, and fish oils. Omega-3 fatty acids are good for the heart, and our body needs DHA for a healthy brain. Infants need DHA, especially during the first 6 months of their lives, so that their brains, eyes, and nervous systems can develop normally. A recent study has shown that there are many positive effects of omega-3 fatty acids in reducing the symptoms of oxidative stress in the respiratory system.
Regular supplementation of omega-3 helps in the reduction of inflammatory cytokines and thus alleviates the effects of COPD. Some comparative studies of omega-3 supplementation versus no omega-3 fatty acids in the diet have demonstrated many positive effects of consuming omega-3 fatty acids. A large group study has also shown the benefits of omega-3 supplementation among smokers with COPD conditions.
Conclusion
Thus, nutritional support in cases of chronic respiratory disorders is of great importance. There are plenty of food sources that are rich in antioxidants, micronutrients, and unsaturated fatty acids. Regular consumption of these foods leads to a better life and reduced symptoms of inflammation. There are many supplements available in the market with clear labels that are easy to consume. Therefore, physical exercise and a healthy diet containing antioxidant-rich nutrients are beneficial.


.png)


