
According to statistics, approximately 425 million adults in the age group of 20–79 years were suffering from diabetes in 2017. This number is expected to rise to 629 million by 2045. Severe obesity is a major risk factor for the development of type 2 diabetes, a disease characterized by insulin resistance, insulin hyposecretion, and hyperglycemia.
Read on to learn more about the connection between obesity and diabetes!
So, What is Diabesity?
Diabesity is a new term describing diabetes in the context of obesity due to the strong association between obesity and diabetes. Sometimes it is also referred to as obesity-dependent diabetes. Recently, diabetes has been recognized as a major public health problem that is evolving to become an epidemic. The number of people suffering from both type 2 diabetes and obesity is rapidly increasing worldwide, mainly due to a sedentary lifestyle.
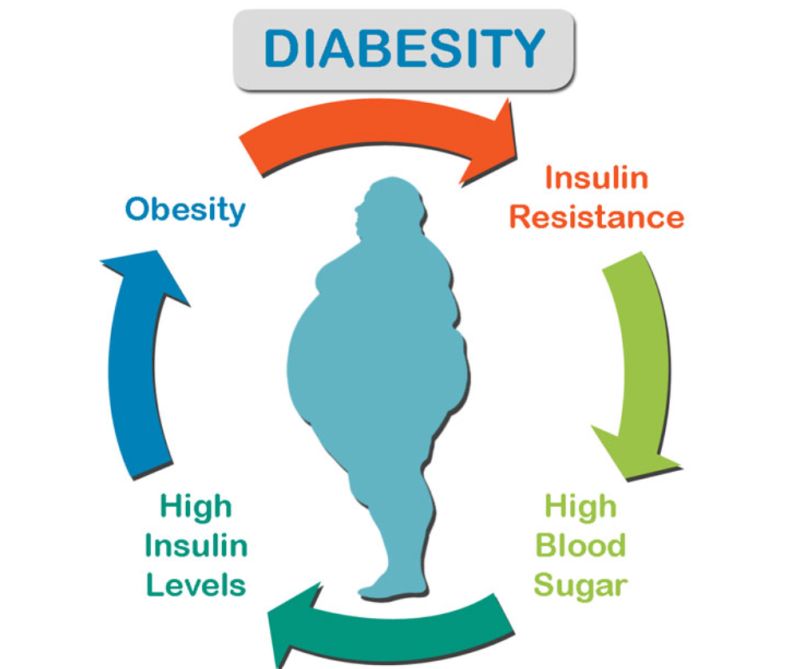
Understanding Diabetes
Diabetes is a condition or disease where there is too much sugar or glucose in the blood. Under normal circumstances, the pancreas releases a hormone called insulin that utilizes the sugar (glucose) from carbohydrates we eat for energy or stores glucose for future use. You can refer to insulin as the "key,” which unlocks the cell to allow sugar to enter and use it for energy.
Insulin helps balance your blood sugar level. If the blood sugar level is too high, a condition called hyperglycemia develops. On the other hand, hypoglycemia is a condition where the sugar level in the body is too low. However, when the pancreas produces very little or no insulin or when the body does not respond to insulin appropriately, it spikes blood sugar levels, causing diabetes.
Types of Diabetes
Generally, there are 2 types of diabetes.
- Type I diabetes: This type occurs when the body fails to produce insulin. Those with type 1 diabetes are insulin-dependent, which means they must take artificial insulin daily to stay alive.
- Type 2 diabetes: Type 2 diabetes, or non-insulin-dependent diabetes, affects the way the body uses insulin. While the body still makes insulin, unlike in type I, the beta cells in the body do not respond to it as effectively.
- According to the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases, this is the most common type of diabetes, and it has strong links with obesity.

Now, What is Obesity?
Obesity is a medical condition that occurs when the fat content is too high in the body, which in turn affects health. Obesity mostly occurs due to a combination of excessive food intake and a lack of physical activity. A Body Mass Index (BMI) between 25 and 29.9 indicates that a person is overweight. A BMI of more than 30 suggests that a person has obesity.
The Link Between Non-Insulin Dependent and Obesity
The risk of developing non-insulin-dependent diabetes is high in people who are overweight or obese. Here, the body makes enough insulin but the cells in the body become resistant to the action of insulin.

Click here to read more about the connection between obesity and insulin resistance.
Studies conducted by Harvard University suggest that obesity causes stress in a system of cellular membranes found inside the cell called the Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER). ER is like a factory for producing protein and a site for processing excess lipids, or blood fats. When the ER has more nutrients to process than it can handle, it sends out an alarm signal, telling the cell to dampen down the insulin receptors on the cell surface. This translates to insulin resistance and increases the concentration of sugar in the blood, thereby developing diabetes. According to Hotamisligil, M.D., Ph.D., Harvard School of Public Health, Boston, "what is actually designed as a short-term adaptive response triggers long-term chronic illness.”
Christopher Newgard, Ph.D., director, of Sarah W. Stedman Nutrition and Metabolism Center explains that it’s the ER’s way of responding when they have to deal with excess nutrients. He adds that this has a downside because insulin soon loses its ability to reduce sugar in the body.
How does “Diabesity” Affect You and What Should You Do?
Obesity is the single biggest trigger for non-insulin-dependent diabetes, but fortunately, even small weight-related changes are very effective. Losing as little as 5–10% of your weight can result in drastic improvements in your overall health and well-being. This, in turn, can reduce your diabetes risk. The following ways can help you reduce the risk of diabetes:
Low-Carb Diets
Focus on low-carb diets. Carbohydrates break down into sugars in the body. In the absence of insulin, this spikes the sugar level in the blood. Reducing the intake of carbohydrates can help you lose weight and prevent type 2 diabetes. You can do this by including whole foods in your diet. Examples include lean protein (chicken or fish), veggies, nuts, seeds, beans, and whole grains.
Learn more about a low-carb diet here!

Vegetarian Diets
Vegetarian diets (no meat, eggs, or dairy) are known to prevent diabesity. A 2-year study of 25,000 people in the United States and Canada concludes that vegans had only one-fourth the risk of developing diabetes as compared to non-vegetarians.

Physical Activities
Include at least one hour of moderate exercise in your daily routine. Regular exercise keeps your body fit and utilizes those carbohydrates to maintain your blood sugar levels.

Avoid Stress
According to Mark Hyman, MD, Director of the Cleveland Clinic’s Center for Functional Medicine, stress is a major unrecognized contributor to insulin resistance and blood sugar imbalance. You should learn to push your pause button every day with deep breathing, visualization, yoga, and other relaxation techniques.

Know more about the yoga poses for diabetes management here!
Conclusion
There is enough research and evidence to show that obesity and diabetes go hand in hand. The obesity epidemic is widely affecting many of us and is a major contributing factor to the development of diabetes. A well-balanced diet combined with exercise and a stress-free lifestyle can go a long way in preventing “diabesity” from becoming an epidemic.
Disclaimer: The information and other content provided in this blog, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment. If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your healthcare provider.


.png)


