When you eat food, glucose is released into the blood. The glucose provides us energy for our day-to-day activities and our body functions. To produce energy, the glucose from the blood must enter the cells. This is made possible with the help of a hormone called insulin, produced by our pancreas. Insulin acts as the "key" that unlocks the "doors" of your cells to enable glucose from your bloodstream to move into your cells. Without insulin, glucose cannot enter your cells but instead accumulates in your blood. This can increase your blood sugar level further, leading to various complications.
Blood Sugar Level
Blood glucose is the amount of sugar in your blood. It comes from the foods you eat, especially carbohydrates like rice, bread, pasta, fruits, vegetables, etc. Our cells need glucose for energy, and we all need it to perform our daily activities. Our brains use about half of our body's energy from glucose. If your pancreas isn't making enough insulin, or if it stops making insulin completely (like in type 1 diabetes), your blood sugar levels can get too high. Or, if your pancreas is making enough insulin but your cells aren't using it right, your blood sugar gets too high.

How do you know your Sugar Levels?
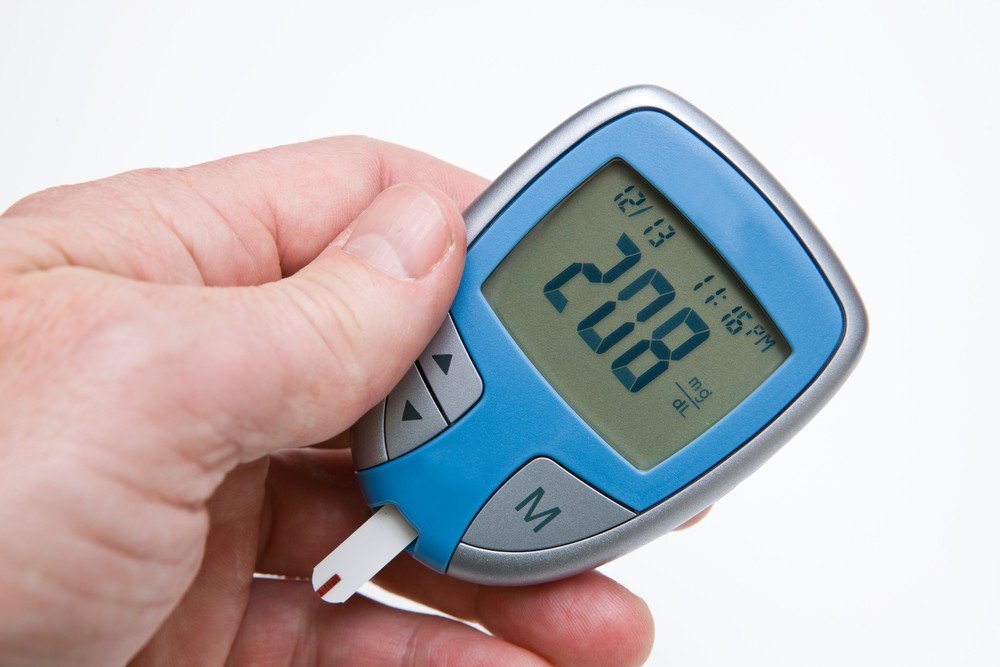
Most of the time, you won't be able to tell what your blood sugar is unless it's really high or really low and starts showing its symptoms. The best way to find out your blood sugar is to use a glucose meter, which is like a finger. You put a drop of blood on a test strip and then stick it into the meter to get a reading. Continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) is another method of monitoring your glucose levels. A continuous glucose monitor (CGM) measures the amount of glucose in your interstitial fluid, which is the fluid between your cells. A CGM is a device that measures your glucose levels every 5 minutes.
Not Too High, Not Too Low - Just Right!
It's really important to keep your blood sugar in a safe range. If it's too low, it can mess with your brain and make it hard to think and act. If your blood sugar is too high and stays high for a long time, it can lead to damage or problems in your body.
Safe range of blood sugar level according to the American Diabetes Association (ADA) guidelines:
Fasting (before eating the first meal of the day) and before meals:
- For diabetic patients, 80–130 mg/dl
- For non-diabetics, below 100 mg/dL
- Postprandial (one to two hours after a meal):
For diabetic patients, less than 180 mg/dl
For non-diabetics, less than 140 mg/dl
Blood Sugar Alert! What to Do at 250 mg/dL
A blood glucose level of more than 130 mg/dl before eating or more than 180 mg/dl two hours after starting a meal is typically regarded as being excessively high. The majority of high blood glucose symptoms, on the other hand, don't manifest until the blood glucose level exceeds 250 mg/dl. A blood sugar level of about 250 mg/dl is considered low and hence requires immediate action. Taking additional insulin is typically one of the best courses of action, as it helps to lessen the effects of high glucose. You must also perform a urine ketone test whenever your blood sugar is over 250 mg/dL to ensure that you are not rapidly approaching diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA). This occurs when there are excess amounts of ketones in the blood, causing the body's blood to become acidic. The most common symptoms of high blood sugar levels include excessive urination, excessive thirst, excessive hunger, weight loss, etc.
Insulin 101
Diabetes is a condition in which your body either cannot produce enough insulin or is unable to use insulin effectively. In that case, your doctor can prescribe insulin therapy. It helps move the excess sugar from the blood, thereby decreasing the blood sugar level. Insulin can be administered in a number of different ways, depending on your individual needs and how you manage your diabetes. You can administer insulin by injection using a pen, vial, or syringe. Dose-deliver insulin via an insulin pump, which is connected to your body via a catheter under the skin. Take insulin as a powder. Your healthcare provider will help you decide which method is right for you.
Is Insulin Therapy Needed?
Insulin therapy is essential for people with type 1 diabetes because it helps to replace the insulin that your body does not make. In some cases, people who have type 2 diabetes or gestational diabetes may need insulin therapy because other treatments have failed to control their blood glucose levels. Insulin therapy reduces the risk of diabetes complications by helping to keep your blood glucose levels within your target range. While insulin therapy can be challenging at times, it’s an effective way to reduce blood sugar levels if you’re having difficulty controlling very low or extremely high blood sugar.
Multiple studies have found that insulin is the most efficient medication to treat excessive glucose levels in patients with diabetes. Thus, putting people on insulin is not a scam unless it is prescribed when it is not needed.
Conclusion
By selecting a proper insulin regimen that works best for you and your lifestyle, you can reduce the risk of diabetes complications and live an active, healthy lifestyle. In addition to this, maintaining a healthy weight, following a nutritious diabetic-friendly diet, and a proper exercise regime are also important to maintain your sugar levels.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. Is putting people on insulin a scam?
No, putting people on insulin is not a scam. Insulin is a crucial hormone for regulating blood sugar levels. Here's why it's important:
- Type 1 diabetes: The body doesn't produce insulin at all. Insulin therapy replaces the missing insulin and is essential for survival.
- Type 2 diabetes: The body may not produce enough insulin or may not use it effectively. Insulin therapy can help manage blood sugar when lifestyle changes like diet and exercise are not enough.
Multiple studies have shown insulin to be the most effective medication for lowering blood sugar in diabetic patients.
2. When might someone need insulin therapy?
Here are some situations where insulin therapy might be recommended:
- High blood sugar levels: If your blood sugar levels are consistently above the recommended range, insulin may be needed to bring them down.
- Type 1 diabetes: As mentioned earlier, insulin is essential for survival in type 1 diabetes.
- Gestational diabetes: In some cases, women with gestational diabetes may need insulin to manage their blood sugar levels during pregnancy.
- Ineffective lifestyle changes: If diet and exercise alone aren't enough to control blood sugar, insulin therapy may be added to the treatment plan.
3. What are some signs of high blood sugar?
While a blood sugar test is the most accurate way to diagnose high blood sugar, some common signs include:
- Frequent urination
- Excessive thirst
- Increased hunger
- Unexplained weight loss
- Fatigue
- Blurred vision
4. What should I do if my blood sugar is high?
If you suspect your blood sugar is high, it's important to see a doctor right away. They can assess your situation and determine the best course of treatment, which may include lifestyle changes or insulin therapy.


.png)


