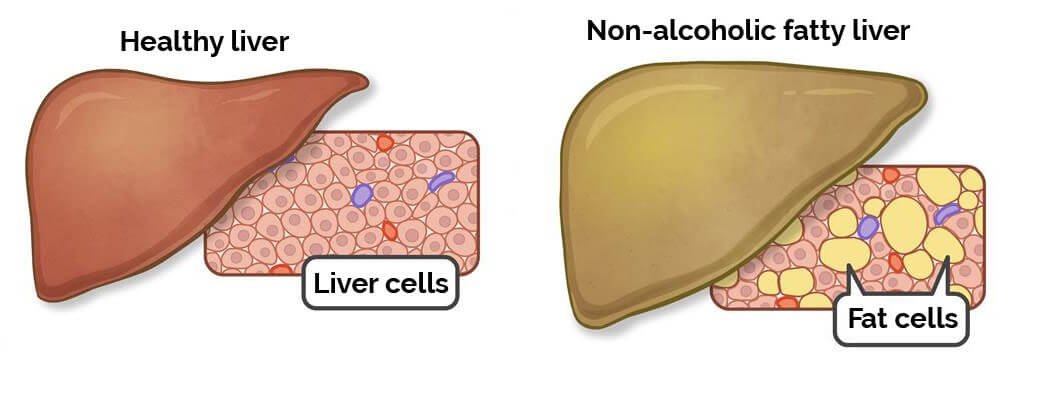
Fatty liver is a condition where excess amounts of fat accumulate in the liver. When the fat accumulation is due to excessive consumption of alcohol, it is called alcohol-related fatty liver. If it is not caused by alcohol consumption, it is called non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Fatty liver disease is more prevalent in people with conditions like obesity and diabetes mellitus.
Symptoms
- Weakness
- Abdominal pain and discomfort
- Abdominal swelling
- Yellowing of skin and eyes
Dietary Guidelines and Lifestyle Modifications
Follow these dietary and lifestyle tips to improve your liver health and your overall well-being:
- Foods rich in saturated fats, like red meat, palm oil, etc., should be taken in moderation. Deep-fried and highly processed foods can be avoided.
- When it comes to unsaturated fats, omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids are more preferable than other forms. Sources of omega-3 fatty acids include salmon, tuna, walnuts, chia seeds, flax seeds, etc.
- Moderate protein consumption can be recommended for fatty livers.
- Intake of foods that are low in glycemic index is recommended, as fatty liver disease is commonly associated with obesity and diabetes.
- The inclusion of small, frequent meals is recommended as it enhances absorption.
- Exercise is essential for everyone, but it is even more important for people with fatty livers. The American Gastroenterological Association recommends individuals with NAFLD have 150–300 minutes of moderate aerobic exercise and 75–150 minutes of vigorous exercise a week.
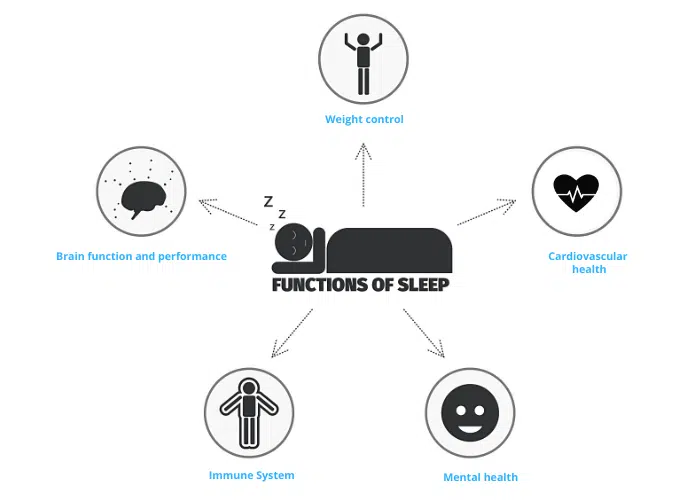
- Sleep is another important factor to consider in liver disease. 7-8 hours of sleep a day is essential, as sleep helps provide the body with the period to rest, heal, and rejuvenate.
Did You Know?
NAFLD is one of the most common liver diseases worldwide, affecting millions of people.
Herbal and Home Remedies
- Green tea: The various elements in green tea, especially catechin, improve the symptoms of fatty liver disease. It helps in eliminating the excess fat in the liver and helps in maintaining liver health.
- Triphala: If you are looking for a natural remedy for fatty liver, Triphala is a great option as it helps regulate digestion and reduce inflammation and oxidative stress caused by the fatty liver.
- Coffee: Coffee is commonly recommended for fatty livers for its hepatoprotective effects that help inhibit the deposition of fats in the liver.
.jpg)
Supplements
- Vitamin D: According to various studies, vitamin D has been proven to reduce inflammation and cholesterol levels in patients with NAFLD.
- Probiotics: Studies have shown that probiotic supplementation lowers liver enzymes, which are high in people with NAFLD.
- Cinnamon: Cinnamon is another supplement shown to lower liver enzymes and improve insulin resistance, inflammation, and cholesterol levels. A study in 2014 suggested that taking 1500 mg of cinnamon daily was effective in improving NAFLD symptoms.
- Garlic: Taking garlic supplements has been proven to lower weight and body fat in people with NAFLD.
- Vitamin E: It is an antioxidant and may have protective effects on the liver.
- Green tea is rich in catechins, which are antioxidants with potential liver-protective properties.
- Milk Thistle: It is a commonly used herb for liver health. It contains a compound called silymarin, which has anti-inflammatory properties.
Conclusion
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is a prevalent condition characterized by the accumulation of fats in the liver unrelated to alcohol consumption. It is often associated with obesity and diabetes. Following a proper diet plan that includes healthy food choices and avoiding saturated fats is crucial. Regular exercise, sufficient sleep, and the incorporation of herbal remedies like green tea, triphala, and coffee can be beneficial. Certain supplements, like vitamin D, probiotics, cinnamon, and garlic, may also aid in managing NAFLD symptoms. However, it is important to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any supplements or making significant dietary and lifestyle changes. Overall, a comprehensive approach that includes a balanced diet, regular exercise, and lifestyle modifications is key to managing NAFLD effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. How is non-alcoholic fatty liver disease diagnosed?
NAFLD is typically diagnosed through a combination of medical history assessment, physical examination, blood tests to check liver enzyme levels and rule out other liver diseases, and imaging tests such as ultrasound, CT scan, or MRI to assess the presence of fat in the liver. A liver biopsy may be performed in some cases to determine the severity of the disease.
2. Can non-alcoholic fatty liver disease be reversed?
Yes, in many cases, NAFLD can be reversed or its progression can be halted through lifestyle modifications. Weight loss, regular exercise, a healthy balanced diet, avoiding or reducing alcohol consumption, managing underlying conditions like diabetes and high cholesterol, and avoiding unnecessary medications can help improve liver health and reduce fat accumulation.
3. Are there any medications or treatments for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
Currently, there is no specific medication approved for the treatment of NAFLD. However, managing underlying conditions such as diabetes, high cholesterol, and obesity can help improve liver health. In some cases, healthcare providers may prescribe medications to manage associated symptoms or address specific risk factors.
4. Can diet and exercise help in managing non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
Yes, adopting a healthy diet and engaging in regular physical activity are key components in managing NAFLD. A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats while limiting processed foods, sugary beverages, and saturated fats can help reduce liver fat and improve overall health. Regular exercise, such as aerobic activity and strength training, can aid in weight loss, reduce insulin resistance, and improve liver function.
5. Are there any complications associated with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?
NAFLD can progress to a more severe form called non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and liver cell damage. NASH can lead to fibrosis (scarring of the liver), cirrhosis (severe scarring and loss of liver function), and, in some cases, liver cancer. Additionally, individuals with NAFLD may have an increased risk of cardiovascular disease and other metabolic conditions.
Reference
- https://www.uofmhealth.org/conditions-treatments/digestive-and-liver-health/fatty-liver-disease-non-alcoholic
- https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/22437-non-alcoholic-fatty-liver-disease
- https://www.mayoclinic.org/diseases-conditions/nonalcoholic-fatty-liver-disease/symptoms-causes/syc-20354567


.png)


