
The history of the olive tree involves a beautiful myth from ancient Greece. The goddess Athena, the namesake of Athens, is said to have planted the original olive tree on the rocky hill that is known today as the Acropolis. Olives have the ability to protect against indigestion, oxidative damage, heart diseases, bone loss, inflammation, arthritis, and various cancers. They also help soothe allergic reactions, improve blood circulation, boost cognitive function, defend against infections, and lower blood pressure.
Olives are a staple ingredient in the Mediterranean diet and are enjoyed in salads, sandwiches, pizzas, or pesto. Table olives (the ones that are not grown for oil extraction) can be consumed as a salty snack or as an appetizer.

The health and medicinal benefits of olives mainly come from iron, calcium, fiber, copper, vitamin E, vitamin K, sodium, choline, phenolic compounds, and oleic acid present in them. Olives are a rich source of antioxidants like hydroxytyrosol, tyrosol, oleanolic acid, and quercetin. They also have a low Glycemic Index (GI).
– Olive is a fruit, not a vegetable.
– Can be green, purple, dark brown, black, or even pink color.
– An olive tree is evergreen and can live up to 2000 years.
– The largest type of olive is called a ‘donkey olive’ and the smallest is known as a ‘bullet’.
Olive oil is extracted from the olive fruit. From ruling our kitchens to taking over the cosmetic world, olive oil has become a rage all over the world in recent times. Olive oil has also proved to be very effective in curing diabetes, breast cancer, cardiovascular diseases, cholesterol, obesity, and kidney stones.
Let’s delve deeper into the health benefits of olives.
Anti-Bacterial Qualities
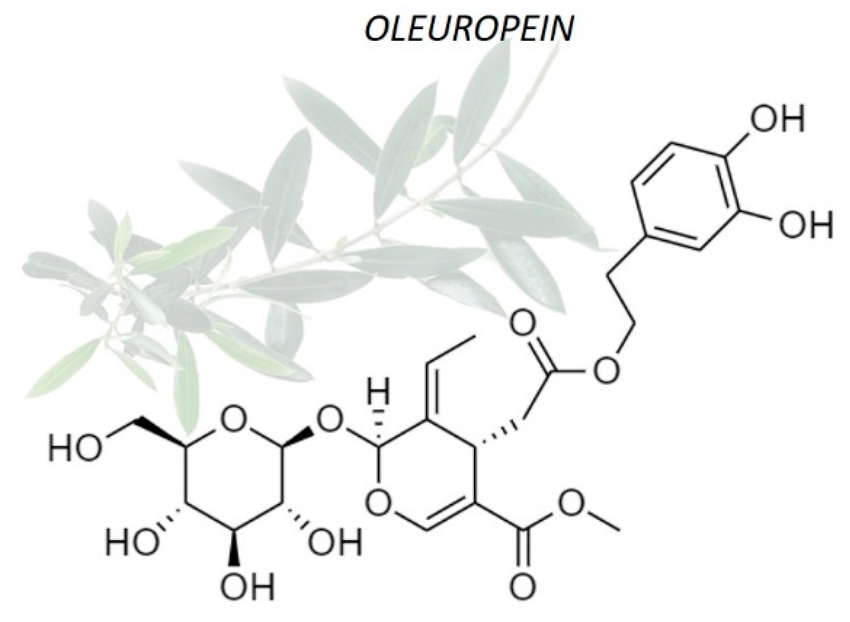
Oleuropein, a valuable chemical component of olives, also functions as an anti-microbial and anti-bacterial agent for the body. Eating plenty of olives increases this chemical, which defends against bacterial infections throughout the body, both internally as well as externally.
Anti-Inflammatory Properties
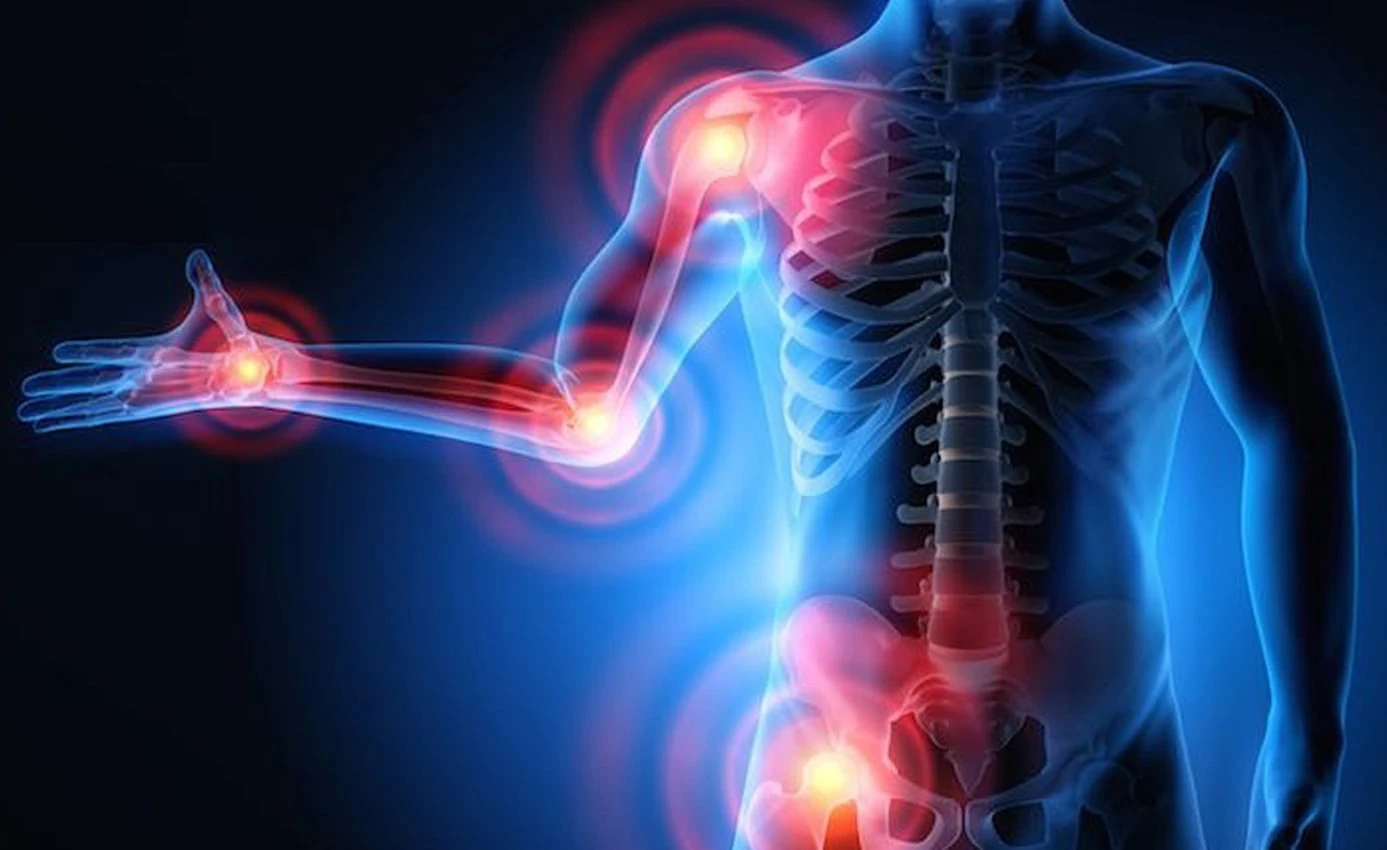
Various compounds in olives function not only as antioxidant compounds but also as anti-inflammatory ones. These reduce inflammation in the body, which includes a reduction in pain and irritation in the joints, muscles, injuries, tendons, and other extremities. Particularly for arthritis, gout, and other rheumatic conditions, olives can be a major benefit, and they alleviate the associated pain.
Good for Heart
Olives contain a monounsaturated fat called oleic acid, which can be helpful in preventing heart disease. Oleic acid lowers blood pressure, reducing the chances of cardiovascular complications as well as general stress on the system.

Furthermore, olives are rich in phenolic compounds, such as hydroxytyrosol, which acts as an anticoagulant. Apart from that, the same phenolic compound also eases the blood vessel tension and dilates the blood vessels, which reduces the strain on the heart and increases blood flow around the body in a healthy way. This ensures the proper functioning and oxygenation of the various organ systems.
Prevents Cancer
Olives contain anthocyanins, which are antioxidants and anti-inflammatory substances. Antioxidants defend the body against free radicals, which mutate healthy cells into cancerous ones. Additionally, oleic acid in olives inhibits certain growth factor receptors that trigger the development of breast cancer.

Promotes Digestion
Olives are a healthy source of fiber. High fiber stimulates peristaltic motion in the intestines, ensuring smooth bowel movements. Fiber also makes you feel full, thereby controlling overeating. Not only can fiber increase your digestive and gastrointestinal health, but it can also help you lose weight. Fiber also boosts heart health by working to eliminate excess cholesterol in the blood.

Anti-Aging Qualities
Intake of olives helps reduce signs of aging such as wrinkles and other skin-related diseases. You can also use olives as an effective skin cleanser. The presence of copper, iron, fiber, and vitamin E, along with other nutrients in them, aids in keeping skin soft and healthy.
_1729959096.jpg)
How can you Include Olives in your Diet?
- Olive tapenade is a delicious and easy-to-make spread that you can use as a dip, sandwich spread, or topping for fish and poultry. To make it, put pitted olives in a food processor with olive oil, garlic, and your favorite seasonings.
- You can toss pasta with chopped olives, tomatoes, garlic, olive oil, and fresh herbs of your choice.
- Marinate olives in olive oil, lemon zest, coriander seeds, and cumin seeds, and enjoy!
- You can add chopped olives to your favorite tuna or chicken salad recipe.
- You can also set out a small plate of olives on the dinner table along with some vegetable crudités for your family to enjoy along with the meal.

Disclaimer: Olives contain high levels of sodium. If you already suffer from high blood pressure or cardiovascular disorders, you should limit the consumption of olives, rather than exacerbating your body with more sodium.
Nutrition Information
100g of olives, green, canned or bottled, pickled provides 145 Calories, Carbs – 3.8g (Dietary Fiber – 3.3g, Sugar – 0.5g), Protein – 1g, Fat – 15g, Sodium – 1556mg
And a percentage daily value of Vitamin A – 8%, Vitamin C –0 %, Iron – 3%, Calcium – 5% (based on a 2000-calorie diet).


.png)


