Do you worry about your prostate's health? Are you at a higher risk of developing prostate cancer? Then, maintaining your prostate health should be a priority. Knowing about the symptoms and risk factors of some of the most common prostate issues will be an invaluable asset to you. But before knowing how to maintain good prostate health, it’s important to understand what the prostate is and what it does.
Read on!
Why is Prostate Health Important?
The prostate is a walnut-sized muscular gland located in between the bladder and penis; it is crucial for the proper functioning of the male reproductive system. The function of the prostate is to secrete a slightly alkaline, milky or white fluid which roughly constitutes 30% of the total seminal fluid volume. This fluid nourishes and maintains your sperm health as well as ensures its motility and longevity. The prostate also contains some smooth muscles that help expel semen during ejaculation.
One of the enzymes in the prostatic fluid is prostate-specific antigen (PSA); after ejaculation, PSA makes thickened semen runnier, helping sperm travel through it more easily. This increases their likelihood of successfully fertilizing an egg. It contains a number of ingredients, including enzymes, zinc, and citric acid.
Although the prostatic fluid is slightly acidic, the other components of semen make it alkaline. This is to counteract the acidity of the vagina as well as protect the sperm from damage. For proper functioning, the prostate needs androgens (male hormones) such as testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT).
Does Age Affect Prostate Health?
Prostate health can deteriorate due to various reasons which can cause diseases like prostatitis, benign prostatic hyperplasia, and prostate cancer. However, there are two major age-related prostate health issues:
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia
The prostate grows naturally with age, usually without problems. However, for some men, the enlarged prostate compresses the urethra, causing benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH). It affects half of the males aged 50 and above. However, BPH does not lead to prostate cancer, nor does it increase the risk. Some common symptoms of BPH or enlarged prostate gland are:
- Difficulty urinating
- Weak urine stream
- Frequent need to urinate, especially at night
- Urinary tract infection
- Stones in the bladder
- Decreased kidney function

Prostate Cancer
As men age, their risk of getting prostate cancer also increases. Damage to the genetic material (DNA) of prostate cells is more likely for men over the age of 55. No one knows why or how prostate cancer starts. About 99% of cases of prostate cancer occur in males over the age of 50. Prostate cancer has many of the same symptoms as an enlarged prostate. Other symptoms may include:
- Pain or burning during urination
- Blood in the urine or semen
- Nagging pain in the back, hips, or pelvis
- Painful ejaculation
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, you should visit a doctor immediately.
Other Risk Factors that affect Prostate Health
In addition to age, there are a few other factors that can affect prostate health. These are:
Hormones
Estradiol, a form of the hormone estrogen, is produced in males as a by-product of testosterone conversion. An imbalance of the estradiol and testosterone ratios increases DHT activity. Excess production of the hormone DHT in the body can increase the risk of BPH, or prostate gland enlargement. Testosterone is converted to form DHT in the body, which promotes the growth of prostate cells. According to experts, DHT levels rise in men as they age, thereby gradually increasing the risk of BPH.
Heredity
Men with a close male relative (father, grandfather, brother, or son) suffering from BPH, or prostate gland enlargement, have a higher risk of getting the disease. The risk increases further if their relatives have symptoms severe enough to require treatment before the age of 60.

Obesity
Several studies suggest that obesity is a risk factor for both prostate gland enlargement and prostate cancer. Obesity or an increase in waist circumference will increase intra-abdominal pressure, which in turn increases bladder pressure, with the potential to exacerbate and worsen prostate enlargement symptoms.

Metabolic Syndrome
It is a cluster of disorders that increase the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases. These disorders include obesity, elevated blood pressure, glucose intolerance, insulin resistance, etc. Researchers discovered that these factors are also risk factors for prostate gland enlargement. Scientists suggest that prostate gland enlargement and metabolic syndrome may be linked to problems with insulin and blood sugar regulation, which result in elevated levels of insulin.

Diabetes
Diabetes that is not well controlled can actually increase the risk of more aggressive prostate cancer. It can also make the symptoms of prostate gland enlargement worse.
A study published in the Journal of Urology showed that men who have diabetes experience worse symptoms of prostate gland enlargement than men without diabetes. Research indicates it may be due to elevated insulin levels and also may be related to the damage that diabetes does to blood vessels.

Poor Diet
A 2008 study published in the American Journal of Epidemiology showed that eating a high-fat diet raised the odds of developing prostate gland enlargement by 31% while eating red meat daily increased the chances by 38%.
Fats can increase the levels of testosterone, estrogen, and other hormones, which have been linked with prostate gland enlargement. Fat is also associated with chronic inflammation, which can cause prostate enlargement and play a role in prostate cancer. Thus, consuming greater amounts of vegetables and lesser amounts of fat and red meat may reduce the risk of developing prostate gland enlargement.
Diagnostic Tests for Your Prostate Health
If you report any abnormalities to your doctor concerning your prostate health, he/she may recommend any of the following diagnostic procedures:
- Physical exam: A physical exam includes a rectal examination that allows the doctor to manually estimate the size and shape of your prostate.
- Urinalysis: Urine check for blood and bacteria.
- Prostatic biopsy: A small amount of prostate tissue is removed to examine it for abnormalities.
- Urodynamic test: Your bladder is filled with liquid via a catheter to measure the pressure of your bladder during urination.
- Prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test: This blood test checks for cancer of the prostate.
- Post-void residual test: This tests the amount of urine left in your bladder after urination.
- Cystoscopy: This is the examination of your urethra and bladder with a tiny lighted scope that is inserted into your urethra
- Intravenous pyelography or urography: This is an X-ray exam or CT scan that is done after a dye is injected into your body. The dye highlights your entire urinary system on the images produced by the X-ray or CT.

How to Improve Prostate Health?
Unfortunately, some of the risk factors and triggers for prostate diseases are difficult to avoid and change. However, you can reduce your chances of falling prey to prostate enlargement or prostate cancer by making some dietary and lifestyle modifications. Some ways to keep your prostate healthy are:
- Eat fewer calories or exercise more to keep your body weight in check and maintain good prostate health.
- Try to keep the amount of fat you get from red meat and dairy products to a minimum.
- Watch your calcium intake. Do not take supplemental doses far above the recommended daily allowance.
- Eat more fish as several studies suggest that fish can help protect against prostate cancer because they have “good fat” particularly omega-3 fatty acids. Also, avoid excess trans fats.
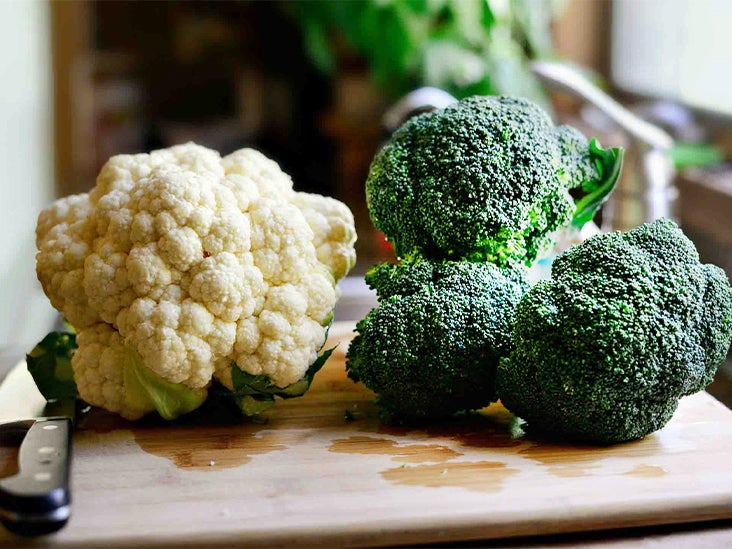
- Try to incorporate tomatoes that are cooked with olive oil, which has been shown to be beneficial. Additionally, include cruciferous vegetables (like broccoli and cauliflower) in your meals. Soy products and green tea are also potential dietary components that would be helpful.
- Avoid smoking and limit caffeine intake as they can worsen your prostate health. Drink alcohol in moderation, if at all.
- Seek expert advice to effectively treat conditions like stress, high blood pressure, diabetes, high cholesterol, and depression. This will reduce your risk of developing prostate cancer and maintain good prostate health.

Conclusion
Men, irrespective of their age, should be concerned about their prostate health. Even though prostate health issues mostly occur after the age of 50, it is never too early to start caring for your prostate health. Follow a healthy lifestyle and diet to maintain good prostate health. However, if you’re suffering from prolonged prostate health issues, then consult a doctor to manage them.
Disclaimer: The information and other content provided in this blog, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment. If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your healthcare provider.


.png)


