
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder that impacts a child's brain function, making it harder for them to pay attention, control impulsive behavior, and organize tasks. These challenges can affect their social skills, communication abilities, and overall behavior, leading to difficulties in daily life.
Parents of children with ADHD in India frequently encounter societal prejudice and a lack of understanding. This, combined with concerns about potential medication side effects, perceived ineffectiveness, and logistical challenges, leads many to halt treatment. As a result, alternative therapies are often explored to manage ADHD symptoms without these associated issues.

Common Symptoms of ADHD
- Inattention: Difficulty focusing, easily distracted, forgetful, and disorganized.
- Hyperactivity: Excessive energy, restlessness, fidgeting, and difficulty sitting still.
- Impulsivity: Acting without thinking, interrupting others, and taking risks.

Treatment Approaches for ADHD
A comprehensive treatment plan typically involves a combination of strategies tailored to the individual's specific needs.
Medication:
- Stimulants: These medications, like methylphenidate and amphetamines, are commonly prescribed to increase focus and reduce impulsivity.
- Non-Stimulants: Options like atomoxetine and alpha-2 agonists can also be effective in managing ADHD symptoms.
Behavioral Therapy:
- Parent Training: Parents learn strategies to manage their child's behavior, set limits, and provide positive reinforcement.
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT): This therapy helps individuals identify and change negative thought patterns and behaviors.
Educational Interventions:
- Individualized Education Plans (IEPs): These plans provide tailored support in the classroom, such as extra time for assignments and preferential seating.
- Organizational Strategies: Techniques like time management, study skills, and note-taking can help individuals with ADHD stay organized.
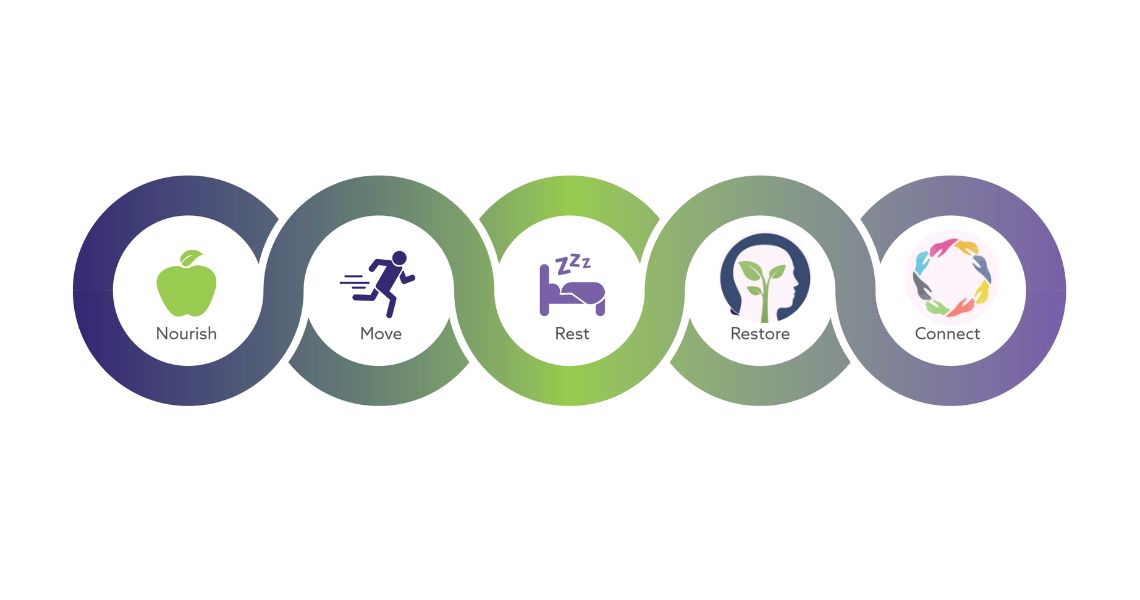
Lifestyle Modifications:
- Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help reduce hyperactivity and improve focus.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet can support brain function and overall well-being.
- Adequate Sleep: Sufficient sleep is essential for cognitive function and emotional regulation.
- Stress Management Techniques: Practices like mindfulness and yoga can help reduce anxiety and improve focus.
Complementary Therapies:
While not proven to be as effective as medication and therapy, some individuals find relief through complementary approaches, such as:
- Dietary Changes: Some people with ADHD may benefit from specific dietary modifications, like limiting sugar intake or following a gluten-free diet.
- Neurofeedback: This technique uses brainwave monitoring to train individuals to regulate their brain activity.
Understanding ADHD from a Functional Medicine Perspective
Functional medicine views ADHD as a multi-faceted condition influenced by genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. Instead of merely treating symptoms, functional medicine aims to find and address the underlying root causes of ADHD. This often includes looking at diet, nutrient deficiencies, gut health, and potential environmental toxins.
The Functional Medicine Approach to ADHD
Functional medicine practitioners believe that ADHD is often caused by underlying imbalances in the body, such as:
- Neurotransmitter imbalances: Neurotransmitters like dopamine and norepinephrine play a crucial role in attention, focus, and behavior. Imbalances in these neurotransmitters can contribute to ADHD symptoms.
- Gut health issues: The gut and brain are connected through the gut-brain axis. Poor gut health, such as leaky gut syndrome or dysbiosis, can lead to inflammation and neurotransmitter imbalances, exacerbating ADHD symptoms.
- Food sensitivities and allergies: Certain food sensitivities or allergies can trigger inflammation and affect brain function, contributing to ADHD symptoms.
- Toxic overload: Exposure to environmental toxins, such as heavy metals or pesticides, can disrupt brain function and contribute to ADHD.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Deficiencies in essential nutrients like omega-3 fatty acids, iron, zinc, and magnesium can impact brain health and contribute to ADHD symptoms.

Functional Medicine Treatment Strategies for ADHD
Functional medicine treatment for ADHD involves a comprehensive approach that may include:
- Dietary interventions: Identifying and addressing food sensitivities or allergies, and optimizing nutrient intake through a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats.
- Gut health support: Using probiotics, prebiotics, and other gut-supportive supplements to improve gut health and reduce inflammation.
- Nutrient supplementation: Addressing any nutrient deficiencies identified through testing, such as omega-3 fatty acids, iron, zinc, and magnesium.
- Neurotransmitter support: Using targeted supplements or lifestyle modifications to support neurotransmitter balance, such as L-tyrosine for dopamine and 5-HTP for serotonin.
- Detoxification: Identifying and addressing toxic exposures and implementing detoxification strategies to remove toxins from the body.
- Lifestyle modifications: Incorporating stress management techniques like yoga, meditation, and regular exercise to improve overall well-being and brain function.
The Importance of Individualized Care
The cornerstone of functional medicine is personalized treatment. There is no one-size-fits-all solution for ADHD, and treatment plans should be tailored to the unique needs of each individual. Functional medicine practitioners will conduct thorough assessments, including blood tests, genetic testing, and lifestyle evaluations, to develop a comprehensive and customized treatment plan.

Conclusion
Functional medicine offers a comprehensive and personalized approach to treating ADHD by addressing the underlying root causes of the disorder. By focusing on restoring balance to the body's systems, functional medicine can help individuals with ADHD improve their symptoms, enhance their quality of life, and achieve long-term well-being.
Disclaimer: The information and other content provided in this blog, or in any linked materials, are not intended and should not be construed as medical advice, nor is the information a substitute for professional medical expertise or treatment. If you or any other person has a medical concern, you should consult with your healthcare provider.
